NOIP 2015 Day 2 详细题解
Published on 2015-11-22感觉网上的题解很不全,只有只言片语,零零散散的,于是自己写了一份。
如果题目有些遗忘了,最好回忆一下题目再看题解。有些题目的解很可能不是最优的,欢迎各路神犇留言。
跳石子
描述
一年一度的“跳石头”比赛又要开始了!
这项比赛将在一条笔直的河道中进行,河道中分布着一些巨大岩石。组委会已经选择好了两块岩石作为比赛起点和终点。在起点和终点之间,有 块岩石(不含起点和终点的岩石)。在比赛过程中,选手们将从起点出发,每一步跳向相邻的岩石,直至到达终点。
为了提高比赛难度,组委会计划移走一些岩石,使得选手们在比赛过程中的最短跳跃距离尽可能长。由于预算限制,组委会至多从起点和终点之间移走 块岩石(不能移走起点和终点的岩石)。
提示
分析
主要考察二分搜索以及贪心的思想。
之前的二分搜索专题本来要说这个题的,结果太懒没完结那个专题。
这是一个最大化最小值问题,可以二分答案。首先在起点和终点放一块石头。
使 表示是否可以安排石头的位置使得最近的两头石头的距离不小于 。
问题就变为求满足 最大的 。由贪心可以知道在满足条件的情况下,两个石头尽量靠近,运用贪心的思想删除石头 。到了最后,如果当前可以删除的石头数量大于等于 那么就成立,否则就不成立。
代码
// Created by Sengxian on 11/21/15. // Copyright (c) 2015年 Sengxian. All rights reserved. // 二分+贪心 #include <iostream> #include <cstring> #include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; const int maxn = 50000 + 10; typedef long long ll; int L, n, m; int pos[maxn]; bool C(int d) { int leftS = m, lastPos = 0; for(int i = 1; i < n; ++i) if(pos[i] - pos[lastPos] < d) leftS--; else lastPos = i; return leftS >= 0; } void solve() { int lb = 0, ub = L + 10; while(ub - lb > 1) { int mid = (lb + ub) / 2; if(C(mid)) lb = mid; else ub = mid; } printf("%d\n", lb); } int main() { scanf("%d%d%d", &L, &n, &m); pos[0] = 0; for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) scanf("%d", &pos[i]); pos[n + 1] = L; n += 2; solve(); return 0; }
题外话
其实官方的数据好弱,要我出数据的我可以卡掉一批人。如果有 ,那么最大距离肯定就是 ,但是根据刚才贪心的思想,当前的 时,如果在中间某处放置了一块石头,那么这块石头到终点就不能满足距离大于 了。而且,不仅仅只有 时,在其他的一些情况也可能这样。
所以,我们判断的依据必须是最后剩余可删除的石头数量,而不是最后一块石头到终点是否距离大于 。
子串
描述
有两个仅包含小写英文字母的字符串 和 。
现在要从字符串 中取出 个互不重叠的非空子串,然后把这 个子串按照其在字符串 中出现的顺序依次连接起来得到一个新的字符串。请问有多少种方案可以使得这个新串与字符串 相等?
注意:子串取出的位置不同也认为是不同的方案。
提示
分析
主要考察动态规划的思想。
设 为串 匹配到第 个位置(位置从 开始),串 匹配到 个位置,而且恰好选串 的 号字符的方案总数。
设 为串 匹配到第 个位置(位置从 开始),串 匹配到 个位置,的方案总数。可以知道 就是要求的答案。
考虑边界,空空相对, 组有一种方法,所以有 。
接下来考虑状态转移方程: 是很容易求出来的。
很好理解, 的方案数目就等于上一个阶段(串 还没有使用第 个位置) 的方案数目,加上串 使用第 个位置的方案总数。
怎么求解 呢?这里运用了类似的最长公共子序列的思想。
如果 ,那么串 的 位置就可以跟 位置合成一组(如果可能的话),这时组数不变;也可以不跟 位置合成一组,自成一组,这时组数+1。所以
如果 呢?根据定义, 要恰好选串 的 号字符,现在选不了,自然为 。所以
综上所述,得到完整的状态转移方程:
最后数组压到二维的就可以省空间了。
代码
这是不压二维的版本,虽然会爆内存,但为了防止三维转二维的某些细节造成困扰,还是发出来。
// Created by Sengxian on 11/21/15. // Copyright (c) 2015年 Sengxian. All rights reserved. // DP #include <algorithm> #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> using namespace std; const int maxn = 1000 + 5, maxm = 200 + 5, moder = 1000000007; int m, n, K; char stra[maxn], strb[maxm]; int f[maxn][maxm][maxm], s[maxn][maxm][maxm]; void solve() { s[0][0][0] = 1; for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { s[i][0][0] = 1; //注意如果不压到二维,这是需要的 for(int j = 1; j <= m; ++j) if(stra[i-1] == strb[j-1]) { for(int k = 1; k <= min(K, j); ++k) { f[i][j][k] = (s[i-1][j-1][k-1] + f[i-1][j-1][k]) % moder, s[i][j][k] = (s[i-1][j][k] + f[i][j][k]) % moder; } }else for (int k = 1; k <= min(K, j); ++k) s[i][j][k] = s[i-1][j][k]; //注意如果不压到二维,这是需要的 } printf("%d\n", s[n][m][K]); } int main() { scanf("%d%d%d%s%s", &n, &m, &K, stra, strb); solve(); return 0; }
压缩后
// Created by Sengxian on 11/22/15. // Copyright (c) 2015年 Sengxian. All rights reserved. // dp after zip #include <algorithm> #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> using namespace std; const int maxn = 1000 + 5, maxm = 200 + 5, moder = 1000000007; int m, n, K; char stra[maxn], strb[maxm]; int f[maxm][maxm], s[maxm][maxm]; void solve() { s[0][0] = 1; for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { for(int j = m; j > 0; --j) if(stra[i-1] == strb[j-1]) { for(int k = min(K, j); k > 0; --k) { f[j][k] = (s[j-1][k-1] + f[j-1][k]) % moder, s[j][k] = (s[j][k] + f[j][k]) % moder; } }else fill(f[j], f[j] + min(K, j) + 1, 0); } printf("%d\n", s[m][K]); } int main() { scanf("%d%d%d%s%s", &n, &m, &K, stra, strb); solve(); return 0; }
旅行计划
描述
公元 2044 年,人类进入了宇宙纪元。
L 国有 个星球,还有 条双向航道,每条航道建立在两个星球之间,这 条航道连通了 国的所有星球。
小 P 掌管一家物流公司, 该公司有很多个运输计划,每个运输计划形如:有一艘物流飞船需要从 号星球沿最快的宇航路径飞行到 号星球去。显然,飞船驶过一条航道是需要时间的,对于航道 ,任意飞船驶过它所花费的时间为 ,并且任意两艘飞船之间不会产生任何干扰。
为了鼓励科技创新,L 国国王同意小 P 的物流公司参与L国的航道建设,即允许小 P 把某一条航道改造成虫洞,飞船驶过虫洞不消耗时间。
在虫洞的建设完成前小 P 的物流公司就预接了 个运输计划。在虫洞建设完成后,这 个运输计划会同时开始,所有飞船一起出发。当这 个运输计划都完成时,小 P 的物流公司的阶段性工作就完成了。
如果小 P 可以自由选择将哪一条航道改造成虫洞,试求出小 P 的物流公司完成阶段性工作所需要的最短时间是多少?
提示
分析
主要考察二分查找、树上倍增、贪心、“树上前缀和”。
题目是一颗树,要求将一条边的权值变为 ,使得所有运输计划的最大时间最小。
直觉告诉我们,这是一个树上倍增的题目,但是它却不像前几年的 Day2 T3 开车旅行那样纯倍增,或许更像疫情控制一些,倍增只是辅助算法,还需要配合其他算法。
由于要使所有运输计划的最大时间最小,不难想到二分答案的方法。
使 表示是否可以改造一条边,使得改造之后所有运输计划中最长的时间不大于 。这是惯用伎俩,用二分的的话,我们就可以确定一个变量 ,正因为有了这个 ,我们才能有的放矢的进行贪心或是干别的。
如何判断 呢?在开始的时候用倍增预处理出所有计划的时间,如果小于等于 ,就可以忽略,如果大于 ,那么就要考虑在其路径上改造一条边。
由于所有时间大于 的计划都要改造一条边,问题就变为了求所有时间大于 的计划的路径交集,改造其中一条最大的边,看看去掉这条边之后,是否可以满足条件。
问题来了,如何求交集呢?
这里给出两种方法,一种是模拟求交集。一种是利用树上前缀和求交集。
方法一
对于两条路径来说,记它们的起始点分别为 ,则它们路径的交集的两个端点只有可能在六个点之间,即 ,我们可以枚举其中两个点,看这条路径是否在都两条路径之中,而且这条路径要尽可能的长。
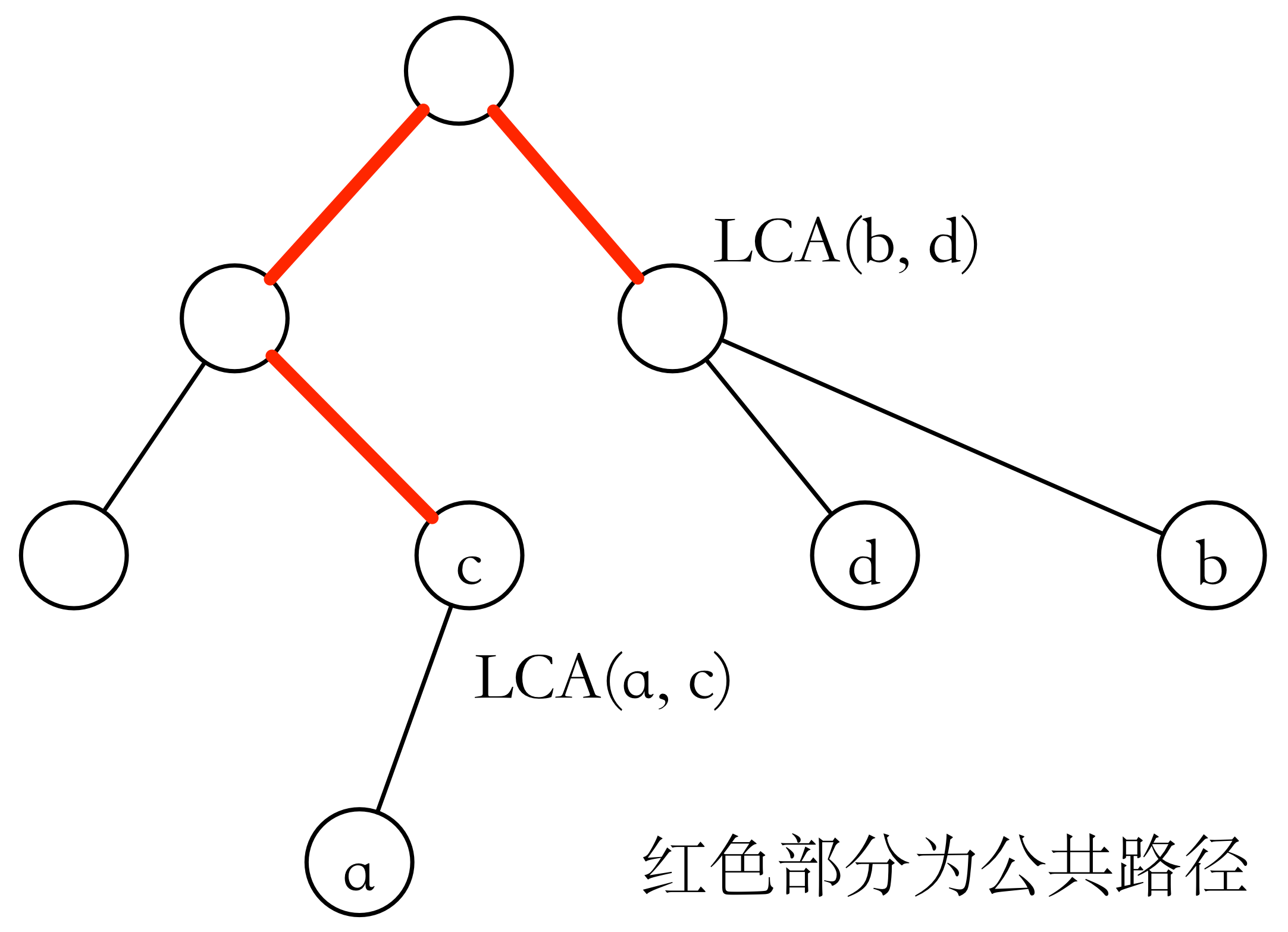
最后所有边按上面的方法顺次求交集就可以了,细节见代码一。
方法二
如果设 为超出时间 的方案数量,边 经过的次数 。对于每个超出时间 的方案,将其路径中边的 加 。最后,所有 的边就是我们要求的的交集。
然而每次给每条边加一肯定是不现实的,所以我们要想出一个高效的方法,来维护边被经过的次数。
这个方法像极了2012年NOIP的 借教室 ,不过是树上的版本。我们先看看借教室的怎么处理区间加减的。
如果要对一段连续区间 同时加上一个值,只需在开始处加上这个值,在结束后减去这个值,维护前缀和就行了。看上去应该是这样的: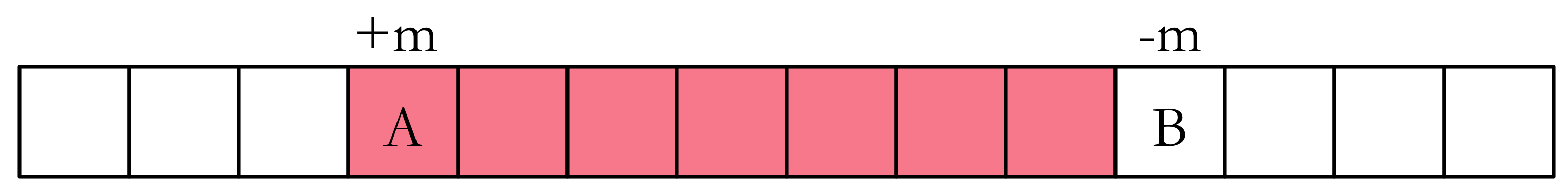
若初始都是 ,让连续区间 同时加上一个值 之后,前缀和 即为元素 的值。下面是前缀和: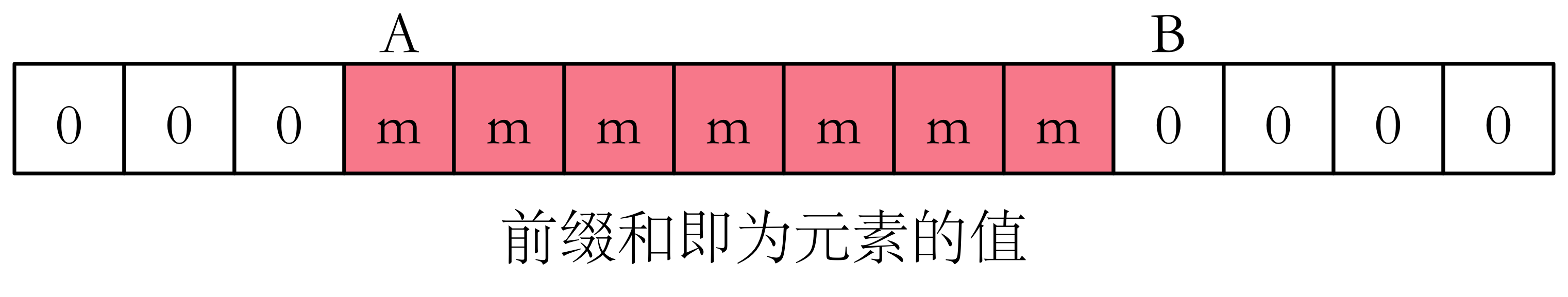
如果有多组加减,也不会冲突。
同样的,在树上,我们用 来表示顶点 到其父亲的这条边被经过的次数, 用于记录顶点信息。
对于每个点对 ,我们将 。
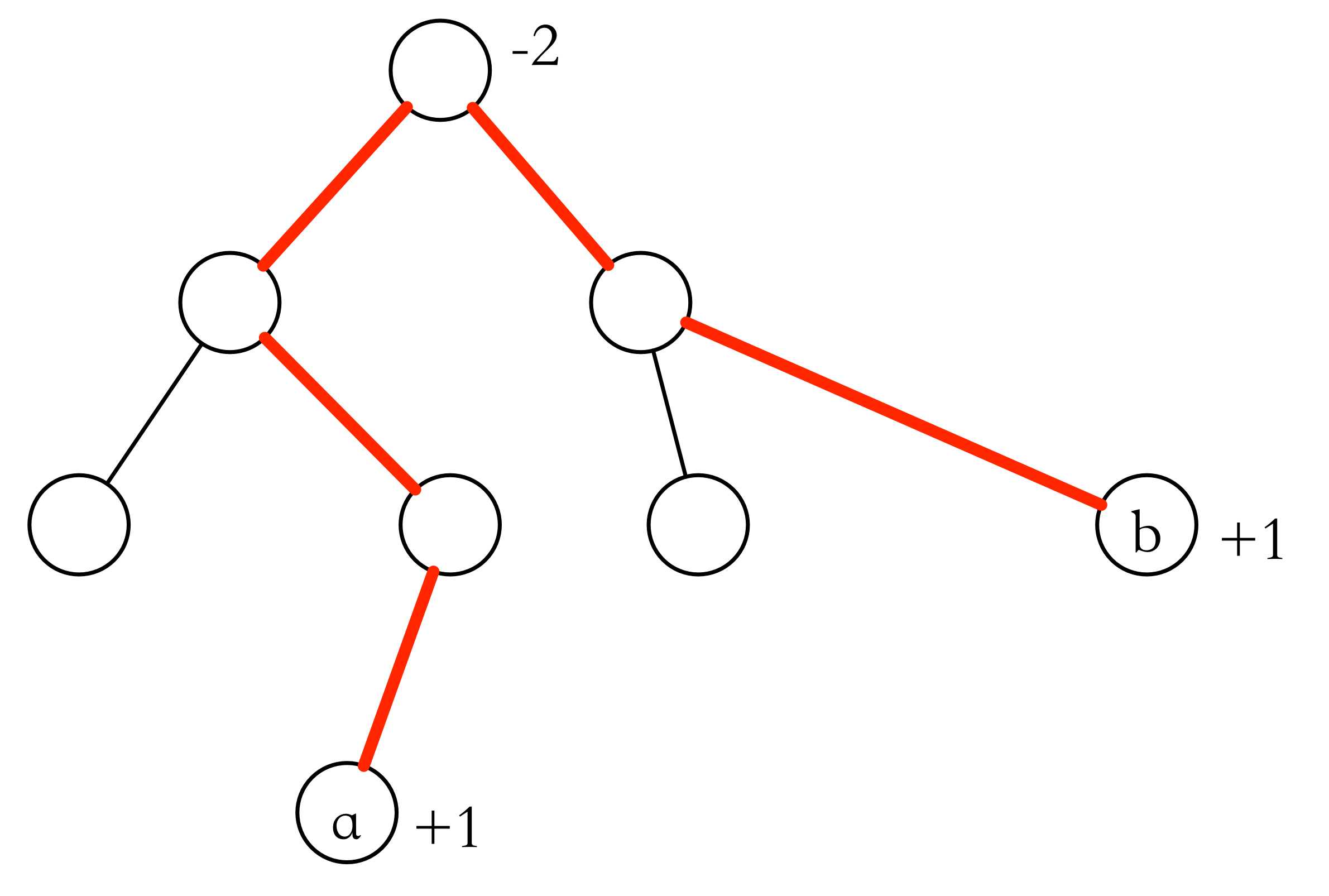
则树上前缀和 。
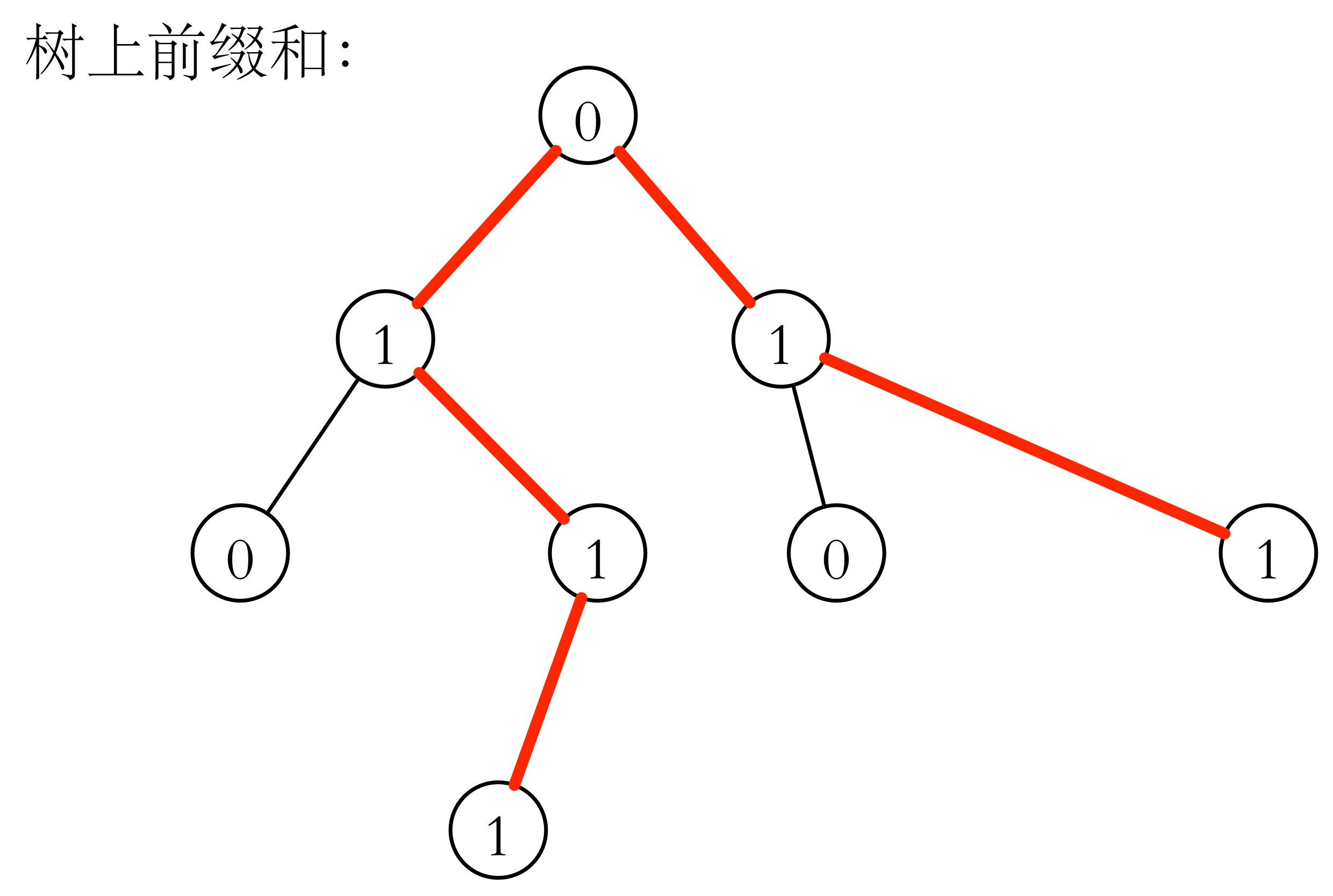
利用 序,对于每个点更新它的父亲的 值,前缀和可以在 的时间内算出来。这样,每条边经过的次数就顺利计算出来了。
这个方法的复杂度是线性的,为 。
代码
方法一:
// Created by Sengxian on 11/21/15. // Copyright (c) 2015年 Sengxian. All rights reserved. // 模拟求交集 #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; const int maxn = 300000 + 5, INF = 1000000000; int n, m; struct edge { int to, cost; }es[maxn * 2]; int first[maxn], nextE[maxn * 2]; int qf[maxn], qt[maxn], qcost[maxn]; int depth[maxn], ancestor[maxn][20], costs[maxn][20], maxCost[maxn][20]; inline int ReadInt() { char ch = getchar(); int n = 0; while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') ch = getchar(); do { n = (n << 1) + (n << 3) + ch - '0'; ch = getchar(); }while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'); return n; } int etmp = 0; inline void addEdge(int f, int t, int c) { es[etmp].to = t; es[etmp].cost = c; nextE[etmp] = first[f]; first[f] = etmp; etmp++; } void dfs(int cur, int fa) { depth[cur] = fa == -1 ? 0 : depth[fa] + 1; ancestor[cur][0] = fa; for(int q = first[cur]; q != -1; q = nextE[q]) { int v = es[q].to; if(v != fa) { maxCost[v][0] = costs[v][0] = es[q].cost; dfs(v, cur); } } } int allCost, maxC, lca; void Query(int a, int b) { if(depth[a] < depth[b]) swap(a, b); int bits = 0, q = 1; while(depth[a] - q > 0) bits++, q *= 2; allCost = maxC = lca = 0; for(int i = bits; i >= 0; --i) if(depth[a] - (1 << i) >= depth[b]) { allCost += costs[a][i]; maxC = max(maxC, maxCost[a][i]); a = ancestor[a][i]; } if(a == b) { lca = a; return; } for(int i = bits; i >= 0; --i) if((depth[a] - (1 << i) >= 0) && ancestor[a][i] != ancestor[b][i]) { allCost += costs[a][i] + costs[b][i]; maxC = max(maxC, max(maxCost[a][i], maxCost[b][i])); a = ancestor[a][i]; b = ancestor[b][i]; } allCost += costs[a][0] + costs[b][0]; maxC = max(maxC, max(maxCost[a][0], maxCost[b][0])); lca = ancestor[a][0]; } void process() { dfs(0, -1); for(int w = 1; (1 << w) < n; ++w) for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) if(depth[i] - (1 << w) >= 0) ancestor[i][w] = ancestor[ancestor[i][w-1]][w-1], costs[i][w] = costs[i][w-1] + costs[ancestor[i][w-1]][w-1], maxCost[i][w] = max(maxCost[i][w-1], maxCost[ancestor[i][w-1]][w-1]); for(int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { Query(qf[i], qt[i]); qcost[i] = allCost; } } inline int Lca(int a, int b) { Query(a, b); return lca; } inline int Length(int a, int b) { Query(a, b); return allCost; } inline int MaxC(int a, int b) { Query(a, b); return maxC; } //is path(a, b) in path(f, t) inline int inPath(int f, int t, int a, int b) { //consider f - t is longer than a - b int len1 = Length(a, f), len2 = Length(b, f); if(len2 < len1) { swap(a, b); len1 = len2; } int len3 = Length(a, b); return (len1 + Length(b, t) + len3) == Length(f, t) ? len3 : 0; } //get the intersection of path(a, b) and path(c, d) 's length inline int Getintersection(int &a, int &b, int c, int d) { int _a = -1, _b = -1, nowLength = 0; vector<int> k; k.push_back(Lca(a, b)); k.push_back(Lca(a, c)); k.push_back(Lca(a, d)); k.push_back(Lca(b, c)); k.push_back(Lca(b, d)); k.push_back(Lca(c, d)); k.erase(unique(k.begin(), k.end()), k.end()); for(unsigned int i = 0; i < k.size(); ++i) for(unsigned int j = i + 1; j < k.size(); ++j) { int l = inPath(a, b, k[i], k[j]); if(l > nowLength && inPath(c, d, k[i], k[j])) { _a = k[i], _b = k[j], nowLength = l; } } a = _a, b = _b; return nowLength; } bool C(int t) { int a = -1, b = -1; for(int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { if(qcost[i] <= t) continue; if(a == -1 && b == -1) a = qf[i], b = qt[i]; else if(Getintersection(a, b, qf[i], qt[i]) <= 0) return false; } int dec = MaxC(a, b); for(int i = 0; i < m; ++i) if(qcost[i] - dec > t) return false; return true; } void solve() { int lb = -1, ub = INF; while(ub - lb > 1) { int mid = (lb + ub) / 2; if(C(mid)) ub = mid; else lb = mid; } printf("%d\n", ub); } int main() { n = ReadInt(), m = ReadInt(); fill(first, first + n, -1); for(int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i) { int f = ReadInt() - 1, t = ReadInt() - 1, c = ReadInt(); addEdge(f, t, c); addEdge(t, f, c); } for(int i = 0; i < m; ++i) qf[i] = ReadInt() - 1, qt[i] = ReadInt() - 1; process(); solve(); return 0; }
代码二(用到了非递归):
// Created by Sengxian on 11/21/15. // Copyright (c) 2015年 Sengxian. All rights reserved. // 树上前缀和 + LCA #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; inline int ReadInt() { static int n, ch; n = 0, ch = getchar(); while (!isdigit(ch)) ch = getchar(); while (isdigit(ch)) n = n * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar(); return n; } const int MAX_N = 300000 + 3, MAX_M = 300000 + 3, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; struct edge { edge *next; int to, cost; edge(edge *next = NULL, int to = 0, int cost = 0): next(next), to(to), cost(cost) {} } pool[MAX_N * 2], *pit = pool, *first[MAX_N]; int n, m; int query_from[MAX_M], query_to[MAX_M], query_cost[MAX_M], query_lca[MAX_M]; int depth[MAX_N], dis[MAX_N], fc[MAX_N], ancestor[20][MAX_N]; int dfsSeq[MAX_N], cnt = 0; void dfs() { static int stk[MAX_N]; static bool vis[MAX_N]; memset(vis, 0, sizeof (bool) * n); int sz = 0; stk[sz++] = 0; ancestor[0][0] = -1, depth[0] = 0, dis[0] = 0; while (sz) { int u = stk[sz - 1]; if (!vis[u]) { for (const edge *e = first[u]; e; e = e->next) { if (e->to != ancestor[0][u]) { depth[e->to] = depth[u] + 1; dis[e->to] = dis[u] + e->cost; fc[e->to] = e->cost; ancestor[0][e->to] = u; stk[sz++] = e->to; } } vis[u] = true; } else dfsSeq[cnt++] = stk[--sz]; } } int work(int a, int b) { if (depth[a] < depth[b]) swap(a, b); int bits = 0, q = 1; while (depth[a] - q > 0) bits++, q <<= 1; for (int i = bits; i >= 0; --i) if (depth[a] - (1 << i) >= depth[b]) a = ancestor[i][a]; if (a == b) return a; for (int i = bits; i >= 0; --i) if ((depth[a] - (1 << i) >= 0) && ancestor[i][a] != ancestor[i][b]) a = ancestor[i][a], b = ancestor[i][b]; return ancestor[0][a]; } void process() { dfs(); for (int w = 1; (1 << w) < n; ++w) for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) if (depth[i] - (1 << w) >= 0) ancestor[w][i] = ancestor[w - 1][ancestor[w - 1][i]]; for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { int LCA = work(query_from[i], query_to[i]); query_cost[i] = dis[query_from[i]] + dis[query_to[i]] - 2 * dis[LCA]; query_lca[i] = LCA; } } int s[MAX_N]; bool C(int t) { int total = 0, maxT = 0; memset(s, 0, sizeof (int) * n); for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) { if (query_cost[i] <= t) continue; total++; s[query_from[i]]++, s[query_to[i]]++, s[query_lca[i]] -= 2; maxT = max(maxT, query_cost[i] - t); } for (int i = 0, u; i < n; ++i) { u = dfsSeq[i]; s[ancestor[0][u]] += s[u]; } int dec = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) if (s[i] == total) dec = max(dec, fc[i]); return maxT <= dec; } void solve() { int l = -1, r = 300000000; while (r - l > 1) { int mid = (l + r) >> 1; if (C(mid)) r = mid; else l = mid; } printf("%d\n", r); } int main() { #ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE freopen("test.in", "r", stdin); #endif n = ReadInt(), m = ReadInt(); for (int i = 0, f, t, c; i < n - 1; ++i) { f = ReadInt() - 1, t = ReadInt() - 1, c = ReadInt(); first[f] = new(pit++) edge(first[f], t, c); first[t] = new(pit++) edge(first[t], f, c); } for(int i = 0; i < m; ++i) query_from[i] = ReadInt() - 1, query_to[i] = ReadInt() - 1; process(); solve(); return 0; }
