UVa 1327 - King's Quest
Published on 2015-12-24描述
从前有一个国王,它有 个王子。皇宫里面还有 个姑娘,并且国王知道每个王子喜欢的姑娘是谁。巫师根据王子喜欢的姑娘,给出了一组可行的方案,使得每个王子都可以与自己喜欢的姑娘结婚。现在国王想知道,每个王子能娶到的姑娘的列表(即其他王子仍可以娶到自己喜欢到的姑娘)。
样例输入
4 2 1 2 2 1 2 2 2 3 2 3 4 1 2 3 4
样例输出
2 1 2 2 1 2 1 3 1 4
附加输入
5 1 3 1 1 3 2 3 5 2 3 4 3 2 1 4 3 1 5 4 2
附加输出
1 3 1 1 1 5 1 4 1 2
分析
这不是稳定婚姻问题!有配对不一定是稳定婚姻问题,稳定婚姻存在一个优先级的排序。当然可以用求婚-拒绝算法,但复杂度极高极高,甚至不如多跑几次完美匹配,TLE 无疑。
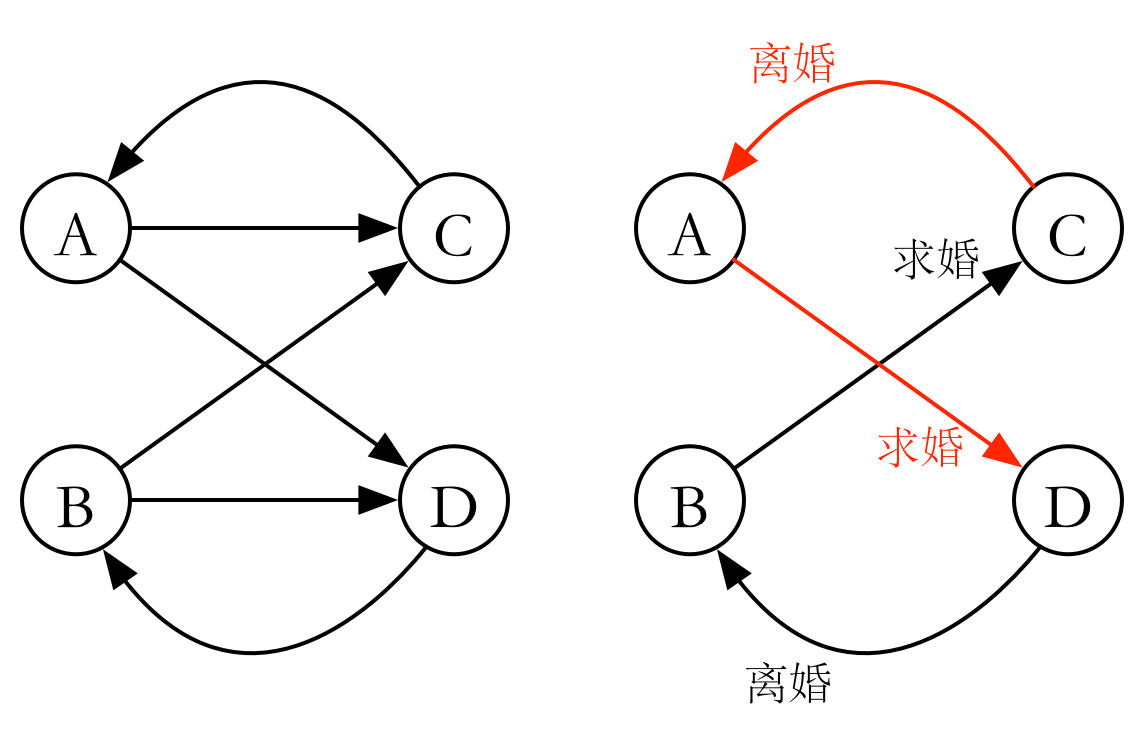
这样考虑,我们手头已经有一个完美方案了,现在有王子 ,方案中他与姑娘 结婚。但他现在想与姑娘 结婚,行不行呢?姑娘 找到他的王子 ,问他能不能够与别人结婚, 恰好可以与 结婚。于是 成功结婚,怎么样,这样就形成了一个圈 。
我们对于王子 喜欢姑娘 ,连边 表示求婚。对于王子 与姑娘 结婚这一现有方案,连边 表示离婚。所以王子 能与姑娘 结婚当且仅当他们在一个强联通分量的时候(即能够形成上文所说的圈)。好好想一想这个求婚-离婚的过程。
代码
// Created by Sengxian on 12/24/15. // Copyright (c) 2015年 Sengxian. All rights reserved. // Uva 1327 强联通分量 #include <algorithm> #include <iostream> #include <cstring> #include <cstdio> #include <cmath> #include <vector> #include <stack> #include <numeric> #include <queue> using namespace std; const int maxn = 2000 + 3, maxNode = maxn * 2; vector<int> G[maxNode]; int n, sccno[maxNode], pre[maxNode], timestamp, scc_cnt; stack<int> stk; inline void tension(int &a, int b) { if(b < a) a = b; } int dfs(int u) { int lowu = pre[u] = ++timestamp; stk.push(u); for(int i = 0; i < G[u].size(); ++i) { int v = G[u][i]; if(!pre[v]) tension(lowu, dfs(v)); else if(!sccno[v]) tension(lowu, pre[v]); //反向边 } if(lowu == pre[u]) { scc_cnt++; while(!stk.empty()) { int x = stk.top(); stk.pop(); sccno[x] = scc_cnt; if(x == u) break; } } return lowu; } void find_scc() { fill(pre, pre + 2 * n, 0); fill(sccno, sccno + 2 * n, 0); timestamp = scc_cnt = 0; for(int i = 0; i < 2 * n; ++i) if(!pre[i]) dfs(i); } inline int ReadInt() { int n = 0, ch = getchar(); while(ch < '0' || ch > '9') ch = getchar(); do { n = n * 10 + ch - '0'; ch = getchar(); }while(ch >= '0' && ch <= '9'); return n; } int main() { int t; while(~scanf("%d", &n)) { //0 ~ n 王子 //n ~ 2n 女孩 for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { G[i].clear(); G[i + n].clear(); t = ReadInt(); while(t--) G[i].push_back(ReadInt() - 1 + n); } for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { G[ReadInt() - 1 + n].push_back(i); } find_scc(); for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { vector<int> ans; for(int j = 0; j < G[i].size(); ++j) if(sccno[i] == sccno[G[i][j]]) ans.push_back(G[i][j] - n + 1); printf("%d", ans.size()); for(int j = 0; j < ans.size(); ++j) printf(" %d", ans[j]); printf("\n"); } } return 0; }
